Species has potential as a ‘winter’ crop
In a recent effort to produce specific pathogen-free (SPF) stocks of the fleshy prawn (Fenneropenaeus chinensis), researchers from two U.S. institutions – the Oceanic Institute in Hawaii and the University of Arizona – collaborated to maintain candidate SPF shrimp through secondary quarantine. With the assistance of the Yellow Sea Fisheries Institute in Qingdao, China, wild broodstock were initially collected from the Yellow Sea and spawned to produce seven maternal families.
Nauplii from each of these families were screened for the presence of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) and Hepatopancreatic Parvovirus (HPV), and transported to a primary quarantine facility at the University of Arizona. The nauplii were reared and analyzed for the presence of specific pathogens using histology and polymerase chain reaction/reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
Pathogens included WSSV, HPV, Yellow Head Virus, Taura Syndrome Virus, and Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus, among others. Shrimp from all seven families tested negative for all listed pathogens on three sequential analyses and were transported to the Oceanic Institute’s secondary quarantine facility in Kona, Hawaii, USA.
Biosecure grow-out module
Shrimp were 0.38 grams when they entered the grow-out module of the secondary quarantine facility. Juveniles from five maternal families and a sixth artificial family composed of shrimp from two original spawns were stocked in separate 230-liter nursery tanks. When shrimp were about 4 grams, they received an internal elastomer tag injected into the sixth abdominal segment. Each family received a unique tag code. After tagging, representative shrimp from all six families were stocked in a 50-square-meter raceway enclosed in a biosecure greenhouse.
The biosecurity features included locked access to the facility, a 4-square-meter antichamber to store and disinfect equipment, the use of dedicated footwear in the greenhouse, and an iodine footbath. A chlorination device and dispersion well handled discharge water.
Growth performance
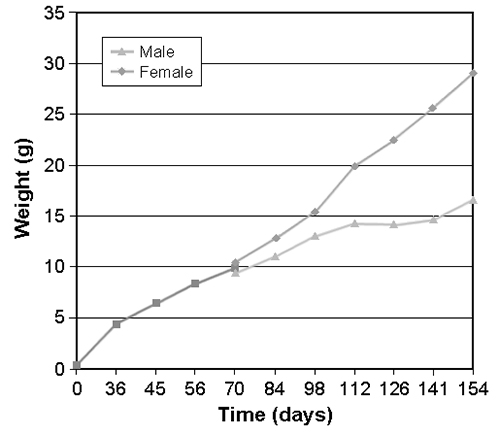
After 155 days in the grow-out module, mean shrimp weight was 23.4 grams, and females were 74 percent larger than males (Fig. 1). Sexual growth dimorphism was not obvious until 113 days after stocking, when at 19.9 grams, females were 38 percent larger than males (14.4 grams).
Mean growth rate for females was 1.3 grams per week throughout the first 155 days in secondary quarantine, whereas growth for males was 0.7 grams per week during the same time period. These growth rates were impressive, considering the water temperature inside the raceway ranged 24 to 26 degrees-C during the first three months, and 22 to 24 degrees-C the following two months.
Maturation/hatchery module
A tentlike structure was erected to enclose the biosecure maturation and hatchery module of the secondary quarantine facility. The maturation recirculation system consisted of a fluidized sand filter, degassing column, sump, bead filter, ultraviolet sterilizer, and chiller to reduce water temperature. About 5 percent of the water was exchanged daily, with effluent discharged through a chlorine contactor.
Forty-five shrimp (30 females and 15 males) were stocked in a 4.5-square-meter maturation tank. Broodstock were then subjected to an acclimation process where they were exposed to 22 degrees-C water, followed by a reduction in water temperature of 1 degrees per day to 17 degrees-C. At this time, unilateral eyestalk ablation was performed on female broodstock, and the water temperature was further reduced at the same rate until it reached 12 degrees-C. After two weeks, the water temperature was raised to 17 degrees-C at 1 degrees per day to induce ovarian development.
The temperature manipulation and ablation procedure stimulated ovarian development, and artificial inseminations were performed on ripe females in an attempt to produce viable napulii. To date, the researchers have produced an F1 generation of F. chinensis from which representative shrimp tested negative for all specifically listed pathogens.
The next step
A major advantage in developing captive SPF shrimp is the opportunity to benefit from domestication and selective breeding. The process of domestication allows the selection of shrimp that are better adapted to the artificial conditions within which they are cultured. The application of selective-breeding techniques offers a tremendous opportunity to improve traits of economic importance, such as growth and disease resistance.
Of particular interest with F. chinensis is their cold tolerance. This species represents a valuable resource for shrimp farmers in temperate and subtropical climates, who could grow a second “winter” crop, thereby increasing production and profitability.
(Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in the April 2003 print edition of the Global Aquaculture Advocate.)
Now that you've reached the end of the article ...
… please consider supporting GSA’s mission to advance responsible seafood practices through education, advocacy and third-party assurances. The Advocate aims to document the evolution of responsible seafood practices and share the expansive knowledge of our vast network of contributors.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Authors
-
Oscar L. Hennig, M.S.
Research Associate, Shrimp Program
The Oceanic Institute
P.O. Box 1423
Kailua-Kona, Hawaii 96745 USA[116,101,110,46,97,118,97,108,64,103,105,110,110,101,104,111]
-
Steve M. Arce
Research Associate, Shrimp Program
The Oceanic Institute
P.O. Box 1423
Kailua-Kona, Hawaii 96745 USA -
Shaun M. Moss, Ph.D.
Research Associate, Shrimp Program
The Oceanic Institute
P.O. Box 1423
Kailua-Kona, Hawaii 96745 USA
Tagged With
Related Posts

Health & Welfare
Selective breeding raises WSSV resistance in fleshy prawns
With the fleshy prawn (Fenneropenaeus chinensis), family selection appears to be a promising prospect that could enhance WSSV resistance.

Health & Welfare
Evaluating heritability of growth, cold tolerance in Chinese white shrimp
Results of this study showed low heritability and a low correlation between growth and cold tolerance traits for Chinese white shrimp juveniles.

Intelligence
Paradigm shifts in shrimp farming
In the evolution of shrimp farming, white shrimp emerged as the primary species. While some farms in the Americas successfully converted to intensive practices, wide adoption has been limited.

Health & Welfare
Born in Hawaii, SPF broodstock shrimp industry faces globalization
The next step for shrimp breeding will be developing animals that aren’t just disease-free, but increasingly resistant to multiple pathogens. The industry is globalizing, with suppliers setting up shop overseas. But its birthplace will always be Hawaii.


